
Skin Allergy Testing
This is less invasive than blood tests and is a good alternative for patients who don’t like needles.
learn more41 % of American adults report having skin allergies.
*According to the National Library of Medicine.
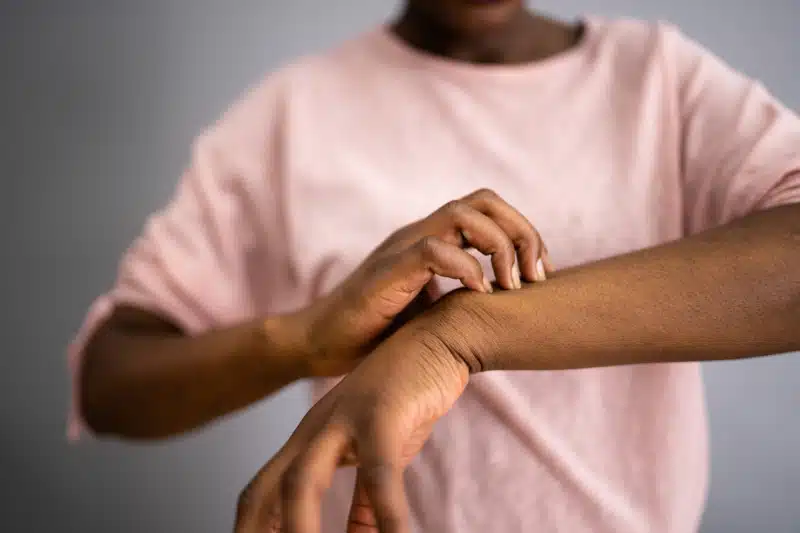
A skin allergy occurs when the immune system overreacts and causes inflammation of the skin. Often, especially in Eczema and in Allergic Contact Dermatitis, the immune system reacts to a foreign substance, known as an allergen. This can lead to an inflammatory response on the skin, resulting in symptoms like rash, redness, itching, and hives.
Common allergens include pollen, pets, mold, drugs, chemicals, latex, and sometimes foods. Sometimes, especially in Hives, there might be an autoimmune cause. These skin rashes can worsen with external factors, such as heat, cold, exercise, pressure, clothing and fabrics, soaps and detergents, and stress.
It is important to note that not all rashes are allergies, but individuals prone to allergies are more susceptible. Skin allergies can be diagnosed and treated by board-certified allergists, who can help identify the cause and provide personalized treatments. Any persistent or unusual skin changes should be checked by a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Skin allergies are caused by an overactive immune response on the skin. Depending on the type of skin allergies, they are often associated with an array of substances known as allergens. These allergens can either be ingested, inhaled, or come directly in contact with the skin.
Here’s a list of some known causes:
Other non-allergen causes include:
To diagnose skin allergies, a board-certified allergist and provider will get a comprehensive history and will do a physical exam, looking closely at your skin.
Your provider might order other testing such as skin allergy testing or patch testing and blood tests. The provider will also rule out other conditions that present similarly. The allergists at AllerVie use a variety of methods to best serve you. Some of our common diagnostics are below.

Skin Allergy Testing
This is less invasive than blood tests and is a good alternative for patients who don’t like needles.
learn more
Blood Testing for Allergies
Blood tests can tell if someone has allergies by finding antibodies in the blood that react to allergens.
learn more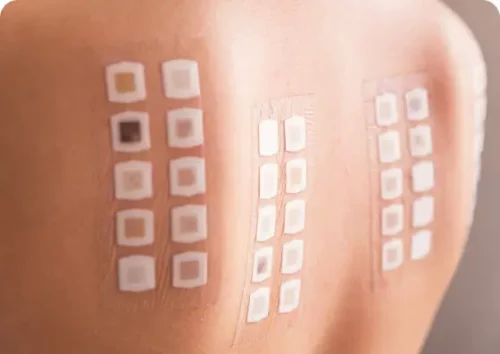
Allergy Patch Testing
Allergy patch testing is a common test used to confirm the cause of allergic contact dermatitis.
learn more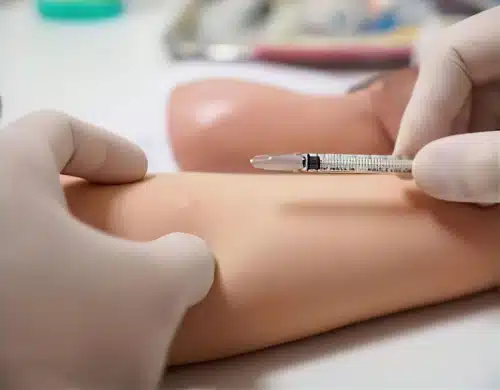
Intradermal Allergy Testing
This is done after a scratch test and involves injecting a small amount of an allergen under the skin.
learn more
Drug Allergy Testing
This involves gradually introducing the medication in small doses until the therapeutic dose is achieved.
learn moreThere are several treatment options available to manage the condition and alleviate symptoms. Remember, scratching can worsen and lead to infection. If your skin allergies are severe or not improving with these treatments, consult your doctor for further evaluation.
Moisturizers
Regularly applying a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer helps keep skin hydrated. Applying moisturizer after a bath helps seal in moisture.
Topical corticosteroids
Apply directly to the skin to help reduce inflammation and itching.
Antihistamines
These medications can help reduce itching and swelling. The second generation of antihistamines are much better than first-generation antihistamines, which have more side effects. These antihistamines are over-the-counter and are available at pharmacies or grocery stores.
Immunomodulators, including biologics
These medications target specific inflammatory pathways that are causing inflammation of the skin. They do not suppress the immune system and have lower side effects than immunosuppressants.
Immunosuppressants, including oral or injectable corticosteroids
In severe cases and with acute exacerbations, medications that suppress the immune system may be necessary to manage eczema symptoms.
Proper bathing
Choose lukewarm water instead of hot water, as it can dry and irritate the skin. Keep baths or showers short and use mild cleansers. Afterward, gently pat dry and apply a fragrance-free moisturizer to lock in moisture. Talk with your allergist about finding a suitable moisturizer and soap.
Wet wraps, soaks, and compresses
They can offer relief for the early, itchy blistered stage of a rash.
Avoid contact
To prevent the reaction from recurring, the key is to avoid contact with the offending material. Your allergist may conduct tests to specifically identify the responsible allergen causing the rash (for example, a patch test), so you know to avoid it in the future.